SEN support at school
What is Special Educational Needs (SEN) Support?
- SEN means Special Educational Needs.
- Some children need extra help to learn at school.
- SEN Support may help children to succeed in class.
This help can include:
- working in a small group
- having extra help from an adult
- using special tools like coloured overlays or laptops
- having a learning plan made just for your child.
Every child or young person identified as having special educational needs should have SEN support. This means help that is additional to or different from the support generally given to other children or young people of the same age.
Some children may have needs in more than one area and these can change over time. Schools must plan support for each area and make sure staff are trained to meet these needs.
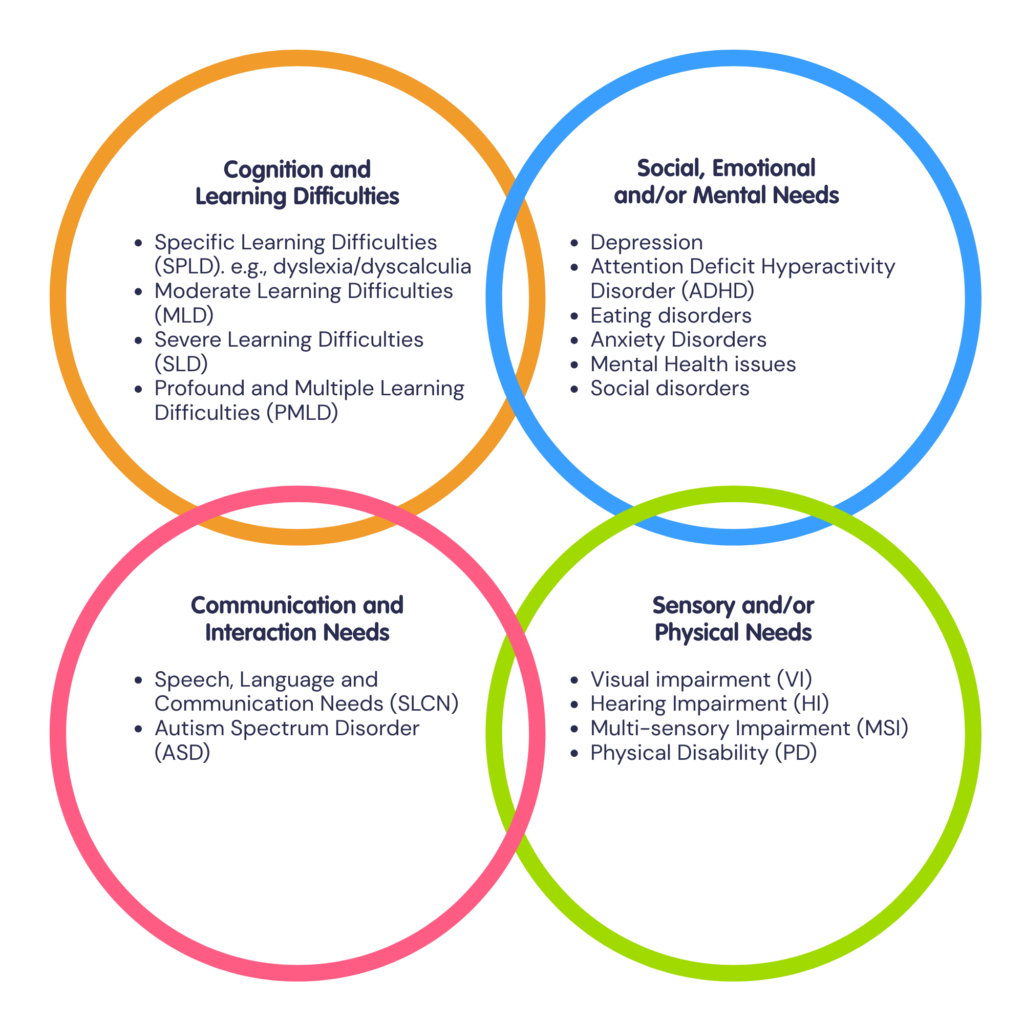
There are four broad areas of need
- Communication and interaction – trouble talking or understanding other
- Cognition and learning – learning things more slowly
- Social, emotional and mental health – struggles with behaviour, anxiety, or emotions
- Sensory and/or physical needs – issues with hearing, vision, or movement.
The graduated approach
SEN support should follows a graduated approach:
Assess – The teacher and SENCO look at what help is needed.
Plan – The school and parents agree on what support will be given.
Do – The school gives the support.
Review – Everyone checks how it’s going and makes changes if needed.
This cycle should happen every term if possible.
What is the process for getting SEN Support?
The school should decide if your child needs SEN support. They should talk to you and your child about this. If a young person is 16 or older then school should involve them directly.
If you think your child needs SEN support, you can ask the school to arrange a meeting to discuss their needs and progress.
These meetings may include:
- regular check-ins with teachers to ensure your views are heard and included in planning support
- reviewing individual support plans to outline specific help needed.
You can verbally request a meeting, however it is sometimes better to send a letter or email to school, addressed to the SENCo.
What SEN Support should I expect for my child?

Children and young people in SEN support can include:
- working in a smaller group
- extra adult help in class
- special learning tools (like visual aids or computers)
- a quiet space to work or take breaks
- help with behaviour or social skills
- speech and language therapy.
What does the law say about SEN Support?

Chapter 6 of the SEND Code of Practice (2015) explains how schools must support children with special educational needs (SEN).
- Schools must support children with special educational needs (SEN), with or without a formal diagnosis. Support should be based on needs.
- This applies to mainstream schools (not special schools)
- Under Section 66 of the Children and Families Act 2014, schools must use their “best endeavours” to meet SEN requirements. This means doing everything they reasonably can to help. Failure to do so, or to make reasonable adjustments under the Equality Act 2010, may be considered discrimination.
- Parents must be included in all decisions
- Children and young people should also be listened to and involved in planning their support.
Schools must:
- check children’s skills and development when they start school
- monitor progress over time
- take action quickly when a child/young person is not making progress.
You can find out more about SEN Support by:
- reading at the schools SEN Information Report. This should be available on their website.
- looking at your local authority’s Local Offer
For further information and support:
IPSEA – How should your nursery, school or college help?



